

Figure 1. Featured Image on the Home Page of Science Advances
The team developed a magnetic drug-delivering thrombolytic nanorobot (HPB-NRs) by modifying heparinoid molecular brushes (PSS) on the surface of superparamagnetic nanoparticles. The PSS on the surface can endow magnetic nanoparticles (MB @ PSS) with high surface charge. These magnetic nanoparticles can be reversibly organized into detachable HPB-NRs clusters under an alternating magnetic field to perform safe targeted therapy for cardiovascular diseases (thrombosis) and to solve fatal problems such as low efficiency and easy bleeding of traditional thrombolytic therapies.
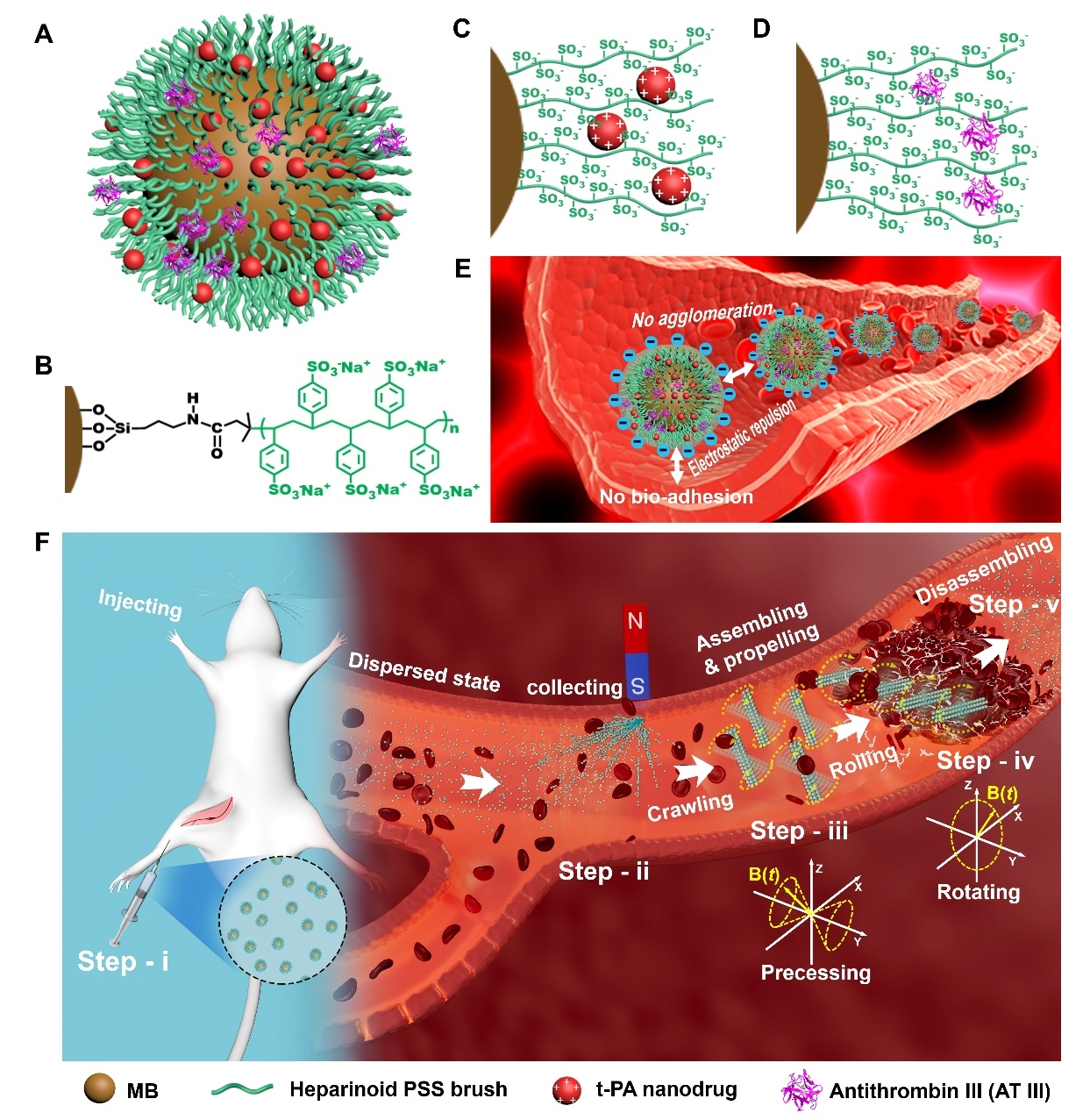
Figure 2. Structure of MB @ PSS Nanoparticles and Targeted Thrombolysis of HPB-NRs Cluster Assembled in Alternating Magnetic Field
This research has laid a foundation for the safe targeted treatment of cardiovascular diseases by nanorobots and brought hope for the future treatment of more challenging cardiovascular diseases, such as cerebral stroke and pulmonary embolism. It is also a forward-looking universal targeted therapy delivery platform that can promote further development of motion-based nanorobots in biomedical applications.
The first author of the paper is Yang Manyi, a doctoral student at the Wuhan University of Technology, Zhang Yaoyu, a master's student at Wuhan University of Science and Technology, as the co-first author and the correspondent authors are Professor Guan Jianguo of Wuhan University of Technology, researcher Mou Fangzhi and Dr. Li Zhi of PLA General Hospital of Central Theater Command.
Link to the article: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adk7251
Written by: Huang Linglin, Guan Jianguo
Rewritten by: Mei Mengqi
Edited by: Wang Jingjing, Li Tiantian
Source: Institute of New Materials (State Key Laboratory of Advanced Technology For Materials Synthesis and Processing)
|
|